How to Charge Two Batteries in Parallel: A Comprehensive Guide
Charging two batteries in parallel can be a practical solution to ensure stable and reliable power for various applications, from marine and RV systems to off-grid solar systems. Properly charging batteries in parallel can extend their lifespan and improve overall efficiency.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of charging two batteries in parallel, covering the necessary steps, precautions, and tips to ensure a safe and effective charging experience.
Table of contents
- 1.What does parallel charging of batteries mean?
- 2.Advantages of parallel charging of batteries
- 3.Step by step instructions for parallel charging of batteries
- 4.Differences between parallel and series batteries
- 5.Precautions before wiring batteries in series or parallel
- 6.Why choose lithium battery from Timeusb?
1.What does parallel charging of batteries mean?
When batteries are connected in parallel, their positive terminals are connected together and their negative terminals are connected as well. This arrangement maintains the same voltage as a single battery but increases the total capacity (ampere hours). For example, two 12V batteries of 100Ah each connected in parallel will still provide 12V but have a total capacity of 200Ah.
2. Advantages of parallel charging of batteries
- Increased capacity: Increases the total ampere hour capacity while maintaining the same voltage.
- Longer battery life: Proper parallel charging can result in longer battery life by balancing the load.
- Redundancy: Provides a backup in case a battery fails and ensures continuous power supply.
3.Step by step instructions for parallel charging of batteries
Parallel battery charging involves connecting multiple batteries to a single charger at the same time. This method can be efficient and convenient, but requires careful handling to ensure safe and effective charging. Here is a detailed guide on how to charge batteries in parallel:
1) Prepare the batteries:
Before starting, make sure that both batteries meet the following criteria:
- Similar capacities: Use batteries with similar capacities to avoid problems with uneven charging.
- state of charge: Ideally, both batteries should have a similar charge level to avoid imbalances.
- Battery type: Use batteries of the same type (e.g. lead-acid battery) to ensure compatibility when charging.
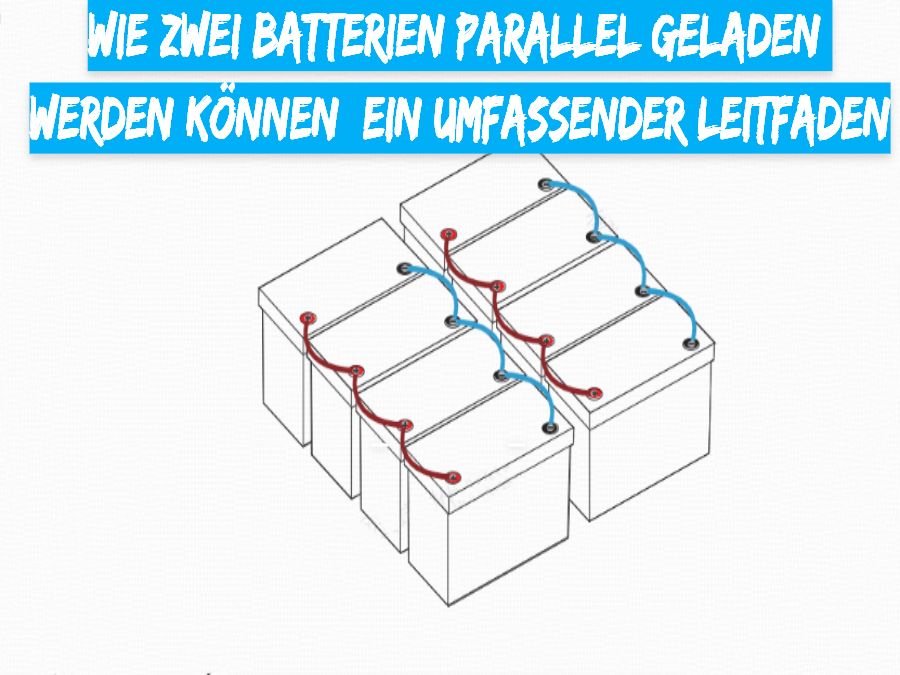
2) Connect the batteries:
Connecting the positive terminals: Use a high-quality cable to connect the positive terminal of the first battery to the positive terminal of the second battery.
Connecting the negative terminal: Use another cable to connect the negative terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second battery.
Secure connections: Make sure all connections are tight and secure to avoid sparking or poor charging performance.
3) Connect the charger:
Positive cable: Connect the positive cable of the charger to the positive terminal of one of the batteries.
Negative cable: Connect the negative cable of the charger to the negative terminal of the other battery.
Charger capacity: Make sure the charger capacity matches or exceeds the combined capacity of the batteries being charged.
Information on the voltage specifications of the various LiFePO4 batteries; and systems can be found in the table below. Visit in the table below. Visit Timeusb charger for LiFePO4 batteriesto find the right charger.

4) Start the charging process:
Check the connections: Check all connections to make sure they are secure and properly insulated.
Turn on the charger: Start charging by turning on the charger once all connections have been checked.
5) Monitoring and maintenance:
Monitor the charging process: Watch the charging process closely, especially if you are charging the batteries in parallel for the first time.
Voltage checks: Regularly check the voltage of each battery with a multimeter to ensure they are charging evenly and within safe limits. Check the terminals and cables: Regularly check the battery terminals and cables for signs of corrosion or damage that could affect performance.
6) Safety tips:
Protective equipment: Always wear gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself from battery acid and possible sparks.
Ventilation: Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area, especially when working with lead-acid batteries.
Supervision: Never leave charging unattended, especially during initial setup or when using new devices.
By following these steps and safety guidelines, you can safely and effectively charge multiple batteries in parallel, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your battery system.
4. Differences between parallel and series batteries
When connecting batteries together, you can do so either in parallel or in series, depending on your specific needs. Both configurations have different characteristics that affect the voltage, capacity, and overall performance of the battery system. Here is a detailed comparison between batteries in parallel and series:
1) Voltage and capacity
Parallel configuration:
- Tension: When batteries are connected in parallel, the total voltage remains the same as a single battery. For example, if you connect two 12V batteries in parallel, the total voltage remains 12V.
- Capacity: The total capacity (measured in ampere hours, Ah) is the sum of the capacities of the individual batteries. Two 12V batteries with a capacity of 100Ah each result in a total capacity of 200Ah.
series connection:
- Tension: In a series connection, the total voltage is the sum of the voltages of all the batteries in the series. For example, if you connect two 12V batteries in series, the total voltage is 24V.
- Capacity: The total capacity is the same as the capacity of a single battery. Two 12V batteries with 100Ah capacity each still deliver 100Ah.
2) Suitability for application
Parallel configuration:
- Use case: Ideal for applications that require higher capacity at the same voltage. This configuration is often used in applications where longer usage time is required, such as solar panels and RVs.
- Advantages: Increases overall capacity, resulting in longer operating times between charges.
Series Configuration:
- Use case: Suitable for applications that require higher voltage. This is commonly used in electric vehicles, power tools and devices that require higher output power.
- Advantages: Increases the overall voltage, allowing motors and devices to operate at higher power.
3) Charging and discharging
Parallel configuration:
- Charge: When charging batteries in parallel, they must be charged evenly to avoid imbalances. It is important to use a charger that can handle the entire combined capacity.
- Unloading: Batteries connected in parallel discharge evenly, provided they are of the same type and age, so that a consistent energy supply is ensured.
series connection:
- Charge: Batteries connected in series should be charged with a charger suitable for the total voltage of the series connection. It is important to monitor each battery to avoid over- or under-charging.
- Unloading: When discharging, all batteries connected in series discharge at the same rate, so a weak battery can affect overall performance.
4) Redundancy and reliability
Parallel configuration:
- Redundancy: Provides better redundancy because if one battery fails, the others can continue to supply power, albeit with reduced capacity.
- Reliability: More reliable in applications where a constant power supply is important as it can better handle battery failures.
Series configuration:
- Redundancy: Less redundancy, because if one battery fails, the circuit can be interrupted, causing the entire system to stop functioning.
- Reliability: Less reliable in terms of redundancy, but necessary for applications requiring higher voltage.
5) Complexity of wiring
Parallel configuration:
- Wiring: Requires more wiring to connect all the positive terminals and all the negative terminals together, but is simple.
- Considerations: Care must be taken to ensure that all connections are secure to avoid short circuits or imbalances.
series connection:
- Wiring: Easier in terms of fewer connections since you connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next.
- Considerations: To avoid problems, it is important to ensure that each battery is balanced and functioning correctly.
5. Precautions before wiring batteries in series or parallel
Whether you are connecting batteries in series or parallel, you must take certain precautions to ensure safety and efficiency. Here is a comprehensive list of precautions to follow:
General precautions for both configurations:
1) Suitable batteries:
Use batteries of the same type, capacity and age to avoid imbalances that could lead to overcharging or undercharging.
- A.Identical batteries with the same battery capacity (Ah) and BMS (A);
- B.The batteries are of the same brand (since different lithium batteries different brands have their own BMS)
- C. were purchased promptly (within one month)
Make sure all batteries have a similar charge level before connecting them.
2) Check the batteries:
Before connecting, check for visible damage, leaks or corrosion. Make sure the terminals are clean and free of corrosion to ensure good contact.
3) Quality of plugs and cables:
Use high-quality connectors and cables that can withstand the expected current load.
Make sure the connections are tight and secure to avoid sparking or poor conductivity.
4) Personal safety:
Always wear protective clothing, including gloves and safety glasses, to protect yourself from battery acid and electrical sparks.
Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling gases that may be released by batteries, especially lead-acid batteries.
5) Tools:
Use insulated tools to avoid accidental short circuits.
Have a multimeter ready to check voltages and make sure connections are correct.
Precautions for series configuration:
1) Voltage compatibility:
Make sure the combined voltage of the batteries does not exceed the rated voltage of your device or charger.
Be careful with higher voltages as they are more dangerous and can cause more severe electric shocks.
2) Charging:
Use a charger suitable for the total voltage of the series connection.
Regularly monitor the voltage of each battery to ensure they are charged evenly and to avoid overcharging or undercharging.
3) Effects of a weak battery:
Note that a weak or damaged battery in the series connection can affect the performance of the entire system, resulting in lower efficiency or failure.
4) Balanced load:
Consider using a battery balancer or equalizer to ensure that all batteries are charged and discharged evenly.
Precautions for parallel configuration:
1) Power processing:
Make sure that cables and connectors can withstand the increased current load caused by parallel connections.
Avoid using cables that are too thin as they may overheat and pose a fire hazard.
2) Uniform charging and discharging:
Make sure the batteries are at a similar charge level before connecting them together to avoid excessive current flow between the batteries, which can cause overheating and damage.
Monitor the charging process closely to ensure that all batteries are charged evenly.
3) Redundancy in case of failures:
Check individual batteries regularly to make sure they are not failing, as one failed battery can cause the other batteries to work harder, leading to possible failures.
Specific safety tips:
Specific safety tips:
1) Avoid short circuits:
Check all connections to make sure there are no short circuits.
Be especially careful with metal tools and jewelry, which can accidentally cause short circuits.
2) Proper ventilation:
Charge and store batteries in a well-ventilated area to avoid the formation of gases that can be dangerous.
3) Fire protection:
In case of emergency, keep a fire extinguisher suitable for electrical fires nearby.
Never charge batteries near flammable materials.
4) Regular maintenance:
To ensure long-term reliability and safety, check and maintain battery terminals and connectors regularly.
Clean the poles of corrosion with a mixture of baking soda and water, then rinse with water and dry thoroughly.
5) Battery specifications:
Always follow the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines for wiring, charging and maintaining your batteries.
By following these precautions, you can ensure safe and effective battery wiring, whether in series or parallel, to meet your power needs reliably and efficiently.
6.Why choose lithium battery from Timeusb?
Timeusb offers technically advanced and cost-effective Lithium Deep Cycle batteries for marine, RV, golf cart and off-grid applications that have the following characteristics
- EV-quality cells certified by UL, FCC, CE, RoSH, UN38.3 with more than 4000 life cycles
- Built-in BMS to protect the batteries against overcharging, overdischarging, overcurrent, overheating, short circuit); protection against undertemperature
- We offer our customers professional technical support, an extensive return policy, understandable operating instructions and a 24-hour online service.





